2016 Все новости SSL
08/12/2016 Leading Certificate Authorities and Microsoft Introduce New Standards to Protect Consumers Online
San Francisco –December 8, 2016 – the Certificate Authority Security Council (CASC), an advocacy group committed to the advancement web security, today announced the Code Signing Working Group has released new Minimum Requirements for Code Signing for use by all Certificate Authorities (CA). These requirements represent the first-ever standardized code signing guidelines. Code signing is the method of using a certificate-based digital signature to sign executables and scripts in order to verify the author’s identity and ensure that the code has not been changed or corrupted. Helping to verify software authenticity and avoid downloading malware and other malicious software is critical to protecting consumers’ online interactions. Microsoft is the first applications software vendor to adopt these guidelines, with others expected to follow. The guidelines include several new features that will help businesses defend their IT systems and information stores from cyber-attacks, including:
- Stronger protection for private keys: The best practice will be to use a FIPS 140-2 Level 2 HSM or equivalent. Studies show that code signing attacks are split evenly between issuing to bad publishers and issuing to good publishers that unknowingly allow their keys to be compromised. That enables an attacker to sign malware stating it was published by a legitimate company. Therefore, companies must either store keys in hardware they keep on premise hardware, or in a new secure cloud-based code signing cloud-based service.
- Certificate revocation: Most likely, a revocation will be requested by a malware researcher or an application software supplier like Microsoft, if they discover users of their software may be installing suspect code or malware. After a CA receives request, it must either revoke the certificate within two days, or alert the requestor that it has launched an investigation.
- Improved code signatures time-stamping: CAs must now provide a time-stamping authority (TSA) and specifies the requirements for the TSA and the time-stamping certificates. Application software suppliers are encouraged to allow code signatures to stay valid for the length of the period of the time-stamp certificate. The standard allows for 135-month time-stamping certificates.
16/11/2016 Symantec took over Blue Coat and its CEO
For 4.65 billion dollars Symantec - the market leader in cyber-security holding branches in more than 40 countries around the world - took over Blue Coat - a company from the same industry, but with a different specialization.
11/11/2016 adgrafics SHA-1 Deprecation Plan by Browsers
Проверьте свой серт на SHA-1, SHA-2
https://proverkassl.com/certificate_ssl_proverka_sha.html
если не повезло ;) ЛЕЧЕНИЕ:
- Go to https://products.websecurity.symantec.com/orders/orderinformation/authentication.do
- Provide the following information requested and click Continue:
- Common Name or Order ID
- Admin Contact's e-mail address associated with the SSL order
- The Image Number generated from the Symantec User Authentication page
- Click Request Access against the correct order ID
- An e-mail will be sent to the Admin Contact's e-mail address specified above
- Click on the link listed in the e-mail to access the User Portal
- Click the Replace Certificate option in the left hand column
PLEASE NOTE: SSL SHA-1 certificates will no longer be issued starting January 1, 2016 to comply with SHA-1 CAB/F Baseline Requirements.
If you're still using SHA-1 certificates, you should replace with SHA-2 certificates.
Major browsers including Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge and Mozilla Firefox will stop supporting these certificates which may mean no access to web sites with SHA-1 certificate.
| Timeline | OS/Browser | SHA-1 expiring in 2016 | SHA-1 expiring on and after January, 1, 2017 |
| As of NOW (Oct. 11, 2016) |
IE 11/Edge on Windows 10 |
Remove the padlock icon |
Remove the padlock icon |
| IE 11 on Windows 7, 8.1 |
Padlock icon still appears |
Padlock icon still appears |
|
Chrome 54 |
Minor error |
Affirmatively insecure |
|
Firefox 49 |
Security warning in web console 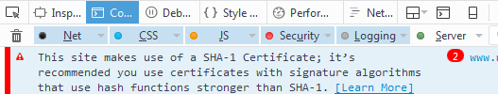 |
Security warning in web console  |
| Timeline | OS/Browser | SHA-1 expiring in 2016 | SHA-1 expiring on and after January, 1, 2017 |
| After January 1, 2017 |
Chrome  |
N/A (expired) |
Block SHA-1 certificates |
Firefox |
N/A (expired) |
Block SHA-1 certificates |
|
| After February 2017 |
IE 11/Edge on Windows 10 |
N/A (expired) |
Block SHA-1 certificates |
You can check your website is ready for the changes at proverkassl.com или
Symantec Crypto Report
If your website currently uses a SHA-1 SSL certificate that expires later than 12/31/2016, you need to take action to protect your business:
Replace your SHA-1 certificate with SHA-256.
If your applications do not support SHA-256, we strong recommend you upgrade them as soon as possible. You can find answers to frequently asked questions below
Question 1:
Currently I have a SHA1 certificate but you’ve sent me the SHA-256 intermediate certificates, what do I do with the new SHA-256 intermediate certificate?
Answer:
If you have a SHA1 certificate, as it is still chained to the SHA1 intermediate, there is no change required. Only if you currently have a SHA-256 end entity certificate do you need to install the SHA-256 intermediate.
Question 2:
What do I need to do for my infrastructure to support SHA-256? Any additional planning or major changes do I need to make?
Answer:
The certificate and private key management for a SHA1 and SHA-256 certificate has not changed. All of the latest servers support SHA-256 and no additional server configuration / resource changes are required to use the SHA 2 certificate. Both the SHA1 and SHA-256 certificate allow the use of more secure protocols such as TLS 1.0, TLS 1.1 and TLS 1.2.
If your server and/or server library is later than the list below you do not need to make any changes to your server configuration:
- Apache server with OpenSSL 0.9.8o+
- Windows Server 2008+
- Windows Server 2003*
- Java 1.4.2+
- Oracle WebLogic 10.3.1+
*Windows servers may require the following patch 938397.
If using XP to connect to the server the following patch may also be required 968730.
For more information on SHA-256 in Windows please view: http://blogs.technet.com/b/pki/archive/2010/09/30/sha2-and-windows.aspx
If your server version is lower than the above please consult your server vendor to upgrade or download the necessary patches. If your server is not listed above, please consult your server vendor if SHA-256 is supported for your server type.
Question 3:
Can we get a production SHA-256 certificate for testing?
Answer:
Unfortunately, we currently do not offer SHA-256 trial certificates and thus a real SHA-256 certificate will need to be purchased. We offer a 30 day refund policy for all our certificates should the SHA-256 certificate not work with your system.
Question 4:
Do you have a checklist of what server software and browser applications are compatible to SHA-256?
Answer:
SHA-256 is currently supported by the following browsers/ software
- Internet Explorer 7+ with Windows XP SP3+
- Safari with Mac OS X 10.5+
- Firefox 1.5+
- Netscape 7.1+
- Mozilla 1.4+
- Opera 9.0+
- Konqueror 3.5.6+
- Mozilla based browsers sine 3.8+
- OpenSSL 0.9.8o+
- Java 1.4.2+ based products
- Chrome 26+
SHA-256 is currently supported by the following servers
- Apache server with OpenSSL 0.9.8o+
- Windows Server 2008+
- Windows Server 2003*
- Oracle WebLogic 10.3.1+
*Windows servers may require the following patch 938397.
If using XP to connect the to the server the following patch may also be required 968730.
For more information regarding SHA-256 and Windows please view : http://blogs.technet.com/b/pki/archive/2010/09/30/sha2-and-windows.aspx
Question 5:
How can I test if a SHA-256 certificate works?
Answer:
The use of the SHA-256 certificate is no different to SHA1. To obtain a SHA-256 certificate the same certificate life cycle process would be used. For the private key and CSR generation and certificate instructions please visit our support pages.
To test the SHA-256 certificate please connect normally to your secured pages using https, using one or more of the SHA-256 supported browser software, for example: www.domain.com Alternatively use our SSL certificate checker found on our support pages.
Question 6:
SHA-256 – is this a Symantec initiative? Is Symantec leading the change for a more secured internet?
Answer:
Symantec is the leader in security and we are committed to be one step ahead of security threats. Many months before Microsoft announced the discontinuation of support for the SHA1 algorithm, Symantec has been preparing for the release of SHA-256 trust chains. In fact our SHA-256 root certificates were ready and installed within many different applications and software. We have and will continue to work with others in the security industry to provide the highest security to safeguard our clients. For the highest security, please have a look at our ECC offers in our website:
http://www.symantec.com/page.jsp?id=how-ssl-works&tab=secTab4
Question 7:
Currently I have a SHA1 certificate and I would like to change it to a SHA-256 certificate, how can I do it?
Answer:
SHA1 certificates can be changed to a SHA-256 certificates via the replacement process.
To replace your certificate to SHA-256, please see the instructions for WebTrust Ukraine and adgrafics klients
Step 1: Generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR)
Click here for assistance with generating a CSR
Note: The Distinguished Name (DN) information on the new CSR must match the original Distinguished Name (DN) information of the certificate you are replacing.
Access the Symantec User Portal for SSL certificate re-issuance
- Go to https://products.websecurity.symantec.com/orders/orderinformation/authentication.do
- Provide the following information requested and click Continue:
- Common Name or Order ID
- Technical Contact's e-mail address associated with the SSL order
Note: If you do not know the Technical Contact's email address, you will need to contact the Reseller that you purchased the certificate with to replace your SSL certificate. - The Image Number generated from the Symantec User Authentication page
- Click Request Access against the correct order ID
- An e-mail will be sent to the Technical Contact's e-mail address specified above
- Click on the link listed in the e-mail to access the User Portal
- Click the Replace Certificate option in the left hand column
Note:If the Replace Certificate option is grayed out in the User Portal please contact the WebTrust Ukraine Customer Support Department to request a manual re-issuance
03/11/2016 adgrafics
Symantec заменяет бесплатно SSL сертификаты пострадавшим клиентам GlobalSign, WoSign и Startcom на сертификаты Symantec Group (Symantec, Thawte, GeoTrust)
23/10/2016 Important Notice Regarding GlobalSign SSL Certificates
GlobalSign will be moving its issuing hierarchy for SSL products back to the default Root-R1 that was affected by the cross certificate revocation last week. That issue has since been resolved and caches have all expired. It is now safe to switch back to Root-R1.
Although GlobalSign will be switching the default issuing CA, you may continue to use your current GlobalSign intermediate. Customers that are experiencing issues with the Root-R3 hierarchy will want to switch to Root-R1 along with this change. Any new orders, renewals, or reissues should begin using the default R1 intermediate provided with your order. This rollback will take place during the following hours:
- BST: 2:00am – 3:00am Monday 24th October 2016
- EDT: 9:00pm –10:00pm Sunday 23rd October 2016
- UTC:1:00am – 2:00am Monday 24th October 2016
15/10/2016 New SHA-1 product - Symantec® Secure Site Pro SHA-1 Private SSL
Symantec® Secure Site Pro SHA-1 Private SSL certificate is offered off of the private CA hierarchies (VeriSign PCA3-G1/G2 Root CA) and allows you to support older, legacy devices and systems that are incompatible with the newer, industry-standard SHA-2 Hashing Algorithm. This certificate is not designed to work with modern browsers. It is available with a full SHA-1 chain and SHA-mixed chain and supports RSA (not DSA or ECC). This solution is perfect for use on private networks like office intranets, for use with network appliances and for a range of other enterprise-level functions.
15/10/2016 adgrafics
Comodo Alters Telephone Verification Process for all OV/EV SSL and Code Signing Certificates Comodo has announced a revision to their OV/EV/Code Signing phone call verification process. They will NO LONGER accept telephone listings from 3rd party directories such as Yellow Pages, 192.com, Manta, etc. or telephone bill statements. They will ONLY verify the company telephone number through Dun & Bradstreet or Legal Opinion Letters. This change is currently live and only applies to new orders and clients.
13/10/2016 adgrafics: GlobalSign OCSP problem
В результате ошибки сотрудников возникла проблема в работе OCSP ... Отчет о происшедшем тут >>>
10/10/2016 adgrafics: The Ongoing WoSign and StartCom Fiasco
- Chinese CA WoSign was found to have violated a series of industry standards.
- Israeli CA StartCom was found to have violated several industry standards.
Что будет с этими CA ? - посмотрим... This document contains additional information, and Mozilla’s proposed conclusion for community discussion, regarding the matter of WoSign and StartCom >>>
21/09/2016 Symantec
At the end of January, 2017, Symantec will be decommissioning our SHA1 RFC 3161 timestamp service, as a result we recommend that all your customers sign their Java applications using SHA256 codesigning certificates and timestamp with our new SHA256 RFC 3161 timestamp service. In the near future, Oracle will be taking steps to remove SHA1 support for both Java signing and timestamping. This will not impact Java applications that were previously signed or timestamped with SHA1, these will continue to function properly, however Java applications signed or timestamped with SHA1 after Oracle’s announced date may not be trusted. In line with Oracle's direction and the general industry removing support for SHA1, Symantec will be decommissioning our SHA1 RFC 3161 timestamp service at the end of January 2017. As a result all your customers are encouraged to move to our new SHA256 RFC 3161 timestamp service without undue delay.
16/09/2016 WebTrust Ukraine - Google’s Plan to Mark Non-Secure Sites
The https://security.googleblog.com/2016/09/moving-towards-more-secure-web.html release of Google Chrome 53 saw the first phase implemented in Google's long-term vision of HTTPS becoming the internet standard. Eventually, every single website without SSL will have a red warning symbol with "Not Secure"
next to it within the Chrome environment. For now, Chrome is marking all non-secure sites with an information radial that
further explains a website has no encryption. This will go a step further starting in January of 2017 for websites with
password or credit card fields.
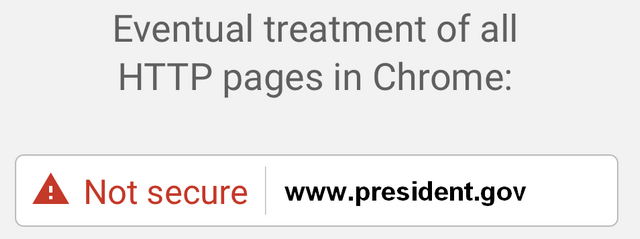
Начиная с января 2017 года, Chrome 56 будет маркировать HTTP страницы где вводится пароль или номер кредитной карты учитывая их особенно уязвимый характер как "не является безопасным," В следующих выпусках HTTP предупреждения будут расширены, например, путем маркировки HTTP-страниц, как "не безопасно" В конце концов планируется пометить все страницы HTTP как незащищенные, и изменить индикатор безопасности HTTP на красный треугольник, который используется для битого HTTPS.
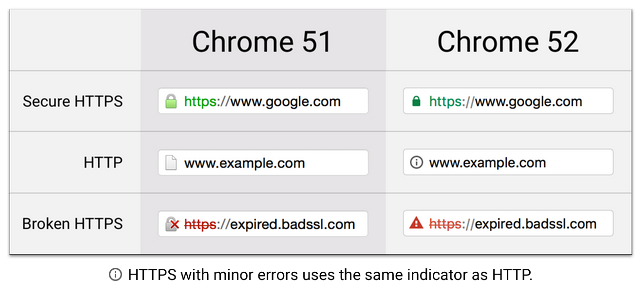
02/08/2016 WebTrust Ukraine - Google меняет значки безопасности в Хроме
Google вносит изменения значок безопасности в строке состояния Chrome. Изменения основаны на
научно - исследовательскую работу , подготовленном сотрудниками Google и Университета Калифорнии, Беркли.
Исследования оценивали сорок семь иконок, бесплатные строки и обследовали 1329 человек.
02/08/2016 WebTrust Ukraine - How do I monitor certificates issued for my domains?
On August 20, 2016, a Certificate Transparency (CT) monitoring feature will be available on the Symantec CryptoReport. This will include the option to do a keyword search (domain name, organization name or serial number) to find all the certificates which have been logged in any of the CT logs. Additionally, it includes the ability to view the certificate details, the CT log details and an option to download the entire set of search results into a Excel file to create actionable reports
* The objective of CT and certificate monitoring is to discover certificates that you do not recognize, to detect those that might have been mis-issued due to internal procedural errors, or detect those that might have been created by a hacker or bad actor. The most common case is procedural error, when someone in your organization purchases and deploys a certificate outside standard procedures. For companies that leverage a discovery tool, such as Certificate Intelligence Center (CIC), mis-issuance is often discovered quickly during routine network scanning and certificate maintenance processes. In the case where a certificate is mis-issued, this mis-issued certificate can be used, in combination with other techniques, to spoof your site or perform man-in-the-middle attacks, which results in real damages to your business or loss of reputation.
02/08/2016 Symantec + Blue Coat
We are extremely pleased to announce that Symantec’s acquisition of Blue Coat has closed, enabling us to immediately move forward as an integrated company. With the closing of this transaction, Symantec is poised to become the most strategic security provider to organizations globally by combining the technology, leadership and go-to-market scale needed to shape the future of security. Press release and more info on https://www.symantec.com/theme/blue-coat-acquisition Symantec Integration Resource Page
21/07/2016 WebTrust Ukraine
Ожидаемы ранее новый стандарт Code Signing Baseline Requirements не был одобрен CA / Browser Forum из-за философских разногласий среди некоторых участников форума, которые считают что разработка правил для CodeSign не входят в сферу интересов и не предусмотрены уставом Форума. В результате было принято решение доработать документ и принять его в рамках CA Security Council (CASC) вне CA / Browser Forum при этом документ получил новое название https://casecurity.org/wp-content/uploads/2016/07/Minimum-requirements-for-the-Issuance-and-Management-of-code-signing.pdf Minimum Requirements for the Issuance and Management of Publicly-Trusted Code Signing Certificates Для хранения ключей будет использоваться FIPS 140-2 Level 2 HSM или его эквивалент а процедура отзыва сертификата предусматривает возможность для третьих лиц ( наблюдателями, поставщиками ПО тощо) а так же изменены требования к сервису метки времени
20/07/2016 Mozilla Adds TLS 1.3 Support in the Developer Edition of Firefox 49
The TLS 1.3 protocol was announced in January by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) when they started working on an official draft. In accordance with this announcement, Mozilla engineers began working on integrating it into their browser back in February. As of this month, this feature is now live in the current Firefox Developer Edition.
08/07/2016 Symantec
Symantec to buy CyberSecurity firm Blue Coat: Greg Clark, Blue Coat’s CEO to Lead Combined Company This week, Symantec announced a definitive agreement to acquire Blue Coat, the #1 market share leader and share gainer in Web Security. Read Announcement and Partner Letter.
08/07/2016 Symantec
On August 20, 2016, a Certificate Transparency (CT) monitoring feature will be available on the Symantec CryptoReport. You will have the option to do a keyword search (domain name, organization name or serial number) and find all the certificates you have logged in any of the CT logs. Additionally, you will be able to view the certificate details, the CT log details and an option to download the entire set of search results into a Excel file so you can create actionable reports as you deem necessary.
08/07/2016 adgrafics
Microsoft adopts CA/B Forum code signing rules. Microsoft has announced that they will adopt the Code Signing Baseline Requirements developed by the CA/B Forum’s Code Signing Working Group. This will take place in February 2017, as part of Microsoft's Root Program Requirements.
08/07/2016 Symantec to disable support for TLS 1.0 seals
As part of commitment to continuous system improvement, Symantec is disabling support for TLS 1.0 across all our seals (Symantec, Thawte and GeoTrust) by the end of August 2016. TLS 1.1 and 1.2 will be supported going forward. Seals will be displayed correctly only on web browsers supporting TLS 1.1 and 1.2
08/07/2016 adgrafics
Google has not yet announced the adoption of name redaction support. So, you may find that Google Chrome issues ""Untrusted"" warnings on certificates with redacted information. However, this shouldn't be an issue for private or internal subdomains. Symantec’s proactive support for name redaction allows you to protect the private nature of applicable domains while maintaining the benefits of monitoring certificates in CT public logs.
07/07/2016 Symantec
From 1st June 2016, name redaction support in Certificate Transparency (CT) became available from all Symantec SSL certs
30/06/2016 adgrafics
Beginning 30th August, GlobalSign will be updating Domain Validated (DV and Alpha) SSL products to comply with the Google CT Policy. GlobalSign will update its DV and Alpha SSL issuance process to publish DV and Alpha SSL Certificates to public CT logs and include Signed Certificate Time-stamp (SCTs) in all issued DV and Alpha SSL Certificates. Certificates issued prior to 30 August 2016 are unaffected and won't be updated or posted
29/06/2016 adgrafics
С 1 декабря в доменах - ICANN’s new transfer policy
- Any changes to first name, last name, organization or email address fields for the owner of any gTLD domain name will now start a trade process
- The process involves obtaining explicit confirmation from current and new registrants before a change can be completed
- After a change of registrant has been completed, previous and new registrant need to receive notifications about the change, with the option of reversing the change
- After a change of registrant has been completed, the domain is by default locked for transfers to a new registrar for the following 60 days
16/06/2016 Symantec
Symantec to Acquire Blue Coat and Define the Future of Cybersecurity
Symantec Enhances Global Leadership Position with Transformational Combination; Delivers Comprehensive Enterprise Cyber Defense Across Critical Threat Vectors and Helps Customers Securely Embrace the Cloud
Greg Clark, Blue Coat CEO, to Lead Symantec Following Closing
Silver Lake to Double Investment to $1 Billion
Bain Capital, Majority Shareholder in Blue Coat, to Reinvest $750 Million in Combined Company and David Humphrey, a Managing Director of Bain Capital, to Join Symantec Board
FY18 Non-GAAP EPS Expected to be $1.70-$1.80, Including $150 Million in Run-Rate Cost Synergies from Blue Coat Transaction Plus Previously Announced $400 Million in Net Cost Savings
21/05/2016 WebTrust Ukraine
On June 1, 2016 all certificates without Certificate Transparency and that are not published in Certificate Transparency logs may cause browser warning messages to display in Google Chrome.
13/05/2016 WebTrust Ukraine о перспективах HTTPS
- Google заявляет что наличие SSL сертификата будет влиять на рейтинг сайта
- Браузеры начнут активно предупреждать пользователей о доступе к незашифрованному сайту
- HTTP / 2 будет поддерживаться только с шифрованием во всех основных браузерах
- SSL / TLS повышает скорость вашего сайта который может значительно увеличить количество переходов
- Gmail предупреждает пользователей, когда электронная почта приходит от незашифрованного сервера электронной почты
13/05/2016 HTTPS Now Mandatory for Geolocation in Chrome Version 50 and Beyond
Chrome 50+ больше не поддерживает получение местоположения пользователя с использованием HTML5 Geolocation API из страниц, поставляемых без защищенных соединений. Это означает, что страница, которая делает API вызов Geolocation должена быть защищена сертификатом SSL
05/05/2016 Symantec Kevin Isaac Senior Vice President, EMEA
Mike Brown will be stepping down as President and CEO. Mike will continue to serve as CEO until a successor has been appointed. Given our solid financial foundation and our successful transformation to a company focused exclusively on cybersecurity, the Board believes that this is the right time to transition leadership for Symantec’s next chapter of growth. The Symantec Board is committed to facilitating a seamless transition, and has formed a search committee to oversee the CEO selection process with the assistance of a leading executive search firm. In addition, to ensure a continued focus on our strategic priorities, the Board has formed an Office of the President, which will allow Symantec’s management team to remain focused on product development and operational excellence while the CEO search is underway. ]
27/04/2016 GlobalSign: Important Notice Regarding In-browser installation of Client Certificates
Important Notice Regarding In-browser installation of Client Certificates. We’d like to notify you of a recent change Chrome has made, which impacts in-browser installation of PersonalSign Client Certificates. In the latest version of Chrome (v.49+), the keygen tag has been depreciated which prevents the generation of keypairs in the Chrome browsers. This has caused an error when customers enroll for PersonalSign Client Certificates using the standard PCKS#7 local keygen method. To avoid this error, users will need to use Internet Explorer or Firefox, or alternatively issue certificates using the PCKS#12 method.
Browser Compatibility
| PKCS #12 (.pfx) Pickup | Browser-Based Installation | PKCS #10 (Provide CSR) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Chrome 1 - 48 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Google Chrome 49+ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| Microsoft Internet Explorer | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Microsoft Edge | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| Mozilla Firefox | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Google Chrome: As of Chrome 49, the < keygen > function has been disabled by default and digital certificate file types are downloaded instead of installed. While the keygen function can manually be enabled, the custom filetype handling is still removed, therefore installation through Google Chrome is not supported.
Microsoft Internet Explorer: IE uses the CertEnroll/XEnroll ActiveX control to generate and install certificates through the browser.
Microsoft Edge: Neither the < keygen > nor the CertEnroll/XEnroll ActiveX controls are present in Microsoft's new Edge browser.
Mozilla Firefox: This browser supports key generation and certificate installation by default through the < keygen > function and special certificate file type handling.
Note: While Firefox supports in-browser certificate installation, it uses its own keystore to store the certificate and is not shared with other applications. Installing through Internet Explorer will install the certificate to the Windows Certificate Store which is used by other applications such as Microsoft Office, Outlook, and Google Chrome. For this reason, Internet Explorer is recommended and is used in the example screenshots.
26/04/2016 Дроклад Trustwave о глобальной безопасности
13/04/2016 Symantec introduces Private CA Hierarchies
In order to comply with CA/Browser Forum requirements, Symantec stopped issuing SHA-1 signed SSL/TLS certificates as of January 1, 2016.
However for customers who run old legacy systems, the migration to SHA-2 can sometimes be very tricky and require extensive upgrades.
This is why Symantec is now providing its channel partners with a Private CA hierarchy which they can offer with Secure Site Pro certificates.
Issuing any SSL/TLS certificate off of the Private CA hierarchies (VeriSign PCA3-G1/G2 Root CA) will allow you to support legacy devices and/or systems that require a SHA-1 certificate.
* Please note that TLS certificates issued off of these hierarchies are not designed to work with modern browsers. Using them with modern browsers could pose a security risk. Modern browsers will regard these certificates as untrusted
12/04/2016 Symantec
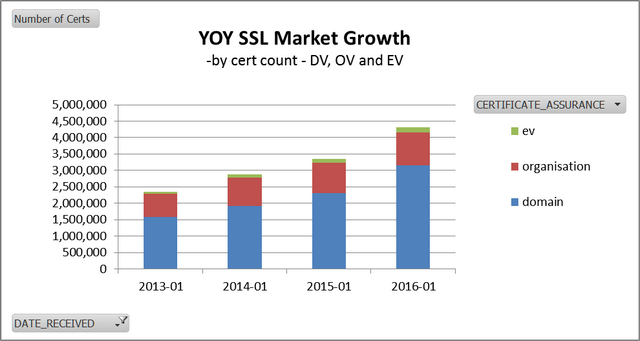
January 2016's Netcraft report found 4,195,909 valid SSL certificates, with a monthly gain of 110,784 (up 2.64%). New certificates accounted for 244,489 across all CA’s during the month. Compared year-on-year with January 2015, we can see the following trends:
- The SSL market grew by 22%
- Total EV units grew by 19%
- Total OV units grew by 7.5%
- Total DV units grew by 27%
12/04/2016 Symantec
Microsoft to remove SSL/TLS trust bit of our VeriSign PCA3-G1 Root At Symantec’s request and in alignment with the industry's migration from less secure 1024-bit roots, Microsoft will remove the SSL/TLS trust bit for our 1024-bit VeriSign Class 3 PCA G1 Root (S/MIME and Code Signing bits will remain trusted). Major browsers started disabling support for 1024-bit roots in September 2014. Microsoft will be implementing this change on April 19, 2016.
10/04/2016 WebTrust Ukraine
Important news for Code Signing security. The CA/Browser Forum's Code Signing Working Group has now completed Version 1 of its Code Signing Baseline Requirements. This is the culmination of over two years' hard work developing and approving the requirements with the Forum. The Group with the objective to 'create a set of baseline requirements for code signing that will reduce the incidence of signed malware' outlined the three goals below to help it achieve this:
- Minimize private key theft by moving towards more secure key storage (protection of private keys)
- Baseline authentication and vetting procedures for all parties
- Information sharing (notification/revocation) for fraud detection (this piece was moved to the Information Sharing Working Group
08/04/2016 Symantec
Symantec is now offering Wildcard SAN certificates exclusively through channel partners>>>
08/04/2016 Symantec
High Value, Low Friction End-to-End Security for Hosting Providers Symantec Encryption Everywhere changes the game – by providing a unified approach to security integration, automation, and management.
01/04/2016 adgrafics
* не ржать ;)
Microsoft, Google, Яндекс и других обяжут установить корневые SSL сертификаты
Российского Центра Сертификации https://lenta.ru/news/2016/02/15/ssl/
27/03/2016 Symantec
At Symantec’s request and in alignment with the industry's migration from less secure 1024-bit roots, Microsoft will remove the SSL/TLS trust bit for our 1024-bit VeriSign Class 3 PCA G1 Root (S/MIME and Code Signing bits will remain trusted). Major browsers started disabling support for 1024-bit roots in September 2014. Microsoft will be implementing this change on April 19, 2016. Symantec's scans found that some Windows clients connecting to public websites and private web servers that are still serving a cross-certificate to the G1 root, may have access issues once the G1 root's SSL/TLS bit is removed.
17/03/2016 Symantec introduces SAN Wildcard certificates
As part of this month’s product release, Symantec is now offering SAN Wildcard certificates, exclusively through channel partners. With the introduction of the Wildcard SAN capability, we are expanding our range of SANs and giving you and your customers more flexibility. Customers now have the ability to add Wildcard SANs to the following OV products:
- Symantec Secure Site
- Symantec Secure Site Pro
- Thawte SSL Web Server
- GeoTrust True Business ID
11/03/2016 Mozilla Definitive Guide to Setting Up SSL/TLS
Mozilla released a Wiki for setting up SSL/TLS properly with best practices. This very comprehensive guide>>> due to the recent DROWN vulnerability being discovered. SSL/TLS
10/03/2016 Notice on Symantec’s Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority G1 (PCA3-G1)
At the end of last year an article was posted on Google’s Online Security blog regarding the Removal of VeriSign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority G1 (PCA3-G1). The information below provides the complete details on the situation for you and your customers. Please contact your Partner Success Manager if you require any additional information or read our http://email.enigma-marketing.co.uk/t/r-l-vtjktud-dyklxtlq-z/ blog
What happened?
As part of the normal course of business, Symantec occasionally evaluates whether certain public root certificates should continue to be in use, or should be repurposed for other non-browser facing applications. Our plan for the 1024-bit PCA3-G1 root is to reuse it in our Private SSL offering to support customers with non-browser legacy applications and devices that are not compatible with SHA-2 certificates.
On November 24, we reached out to all of the major browsers, including Google (except for Mozilla who had already begun to remove untrusted roots in 2014) to request that they remove or un-trust our PCA3G1 root.
Why did we ask them to remove the root from their trust stores?
It’s based on older, lower strength security that is no longer recommended. It hasn’t been used to generate new certificates in years, and it was no longer pertinent to their users.
Did Symantec violate CA/B Forum business requirements?
Our request to the browsers did not violate any CA/B Forum BR's. We asked the browser community to take root Certificate PCA3G1 out of circulation for the above reasons and to stay within compliance of industry guidelines.
Our intent is to use this root to issue SHA-1 certificates in 2016 to customers who have expressed that need for their non-browser applications. To be used for that purpose in compliance with CA/B Forum guidelines, the root must no longer be trusted in browsers. That's why we have asked browsers to remove the root. The certs we will issue from this root are not intended for use with browsers and will not cause any harm to users of browsers who remove or un-trust the root.
Symantec's November Media Statement
In November, Symantec notified major browsers, including Google, that they should remove or un-trust a legacy root certificate from
their lists called the VeriSign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority G1 (PCA3-G1). We advised this action because this
particular root certificate is based on older, lower strength security that is no longer recommended, hasn’t been used to generate
new certificates in several years, and will now be repurposed to provide transition support for some of our customers’ legacy,
non-browser applications. These roots have been phased out per the CA/Browser Forum Baseline Requirements, so removing them
is in keeping with industry standards and best practices, not because of some flaw or issue. Google has indicated that they
intend to do exactly as we requested, a step that other browsers started taking in 2014. For more information visit our
https://knowledge.symantec.com/support/ssl-certificates-support/index?page=content&id=ALERT1941&actp=LIST&viewlocale=en_US knowledge base
07/03/2016 Changes associated with Code Signing certificates
Changes associated with Code Signing certificates On Windows 7 platforms and above, the following are new guidelines from Microsoft:
- Microsoft will no longer allow new SHA-1 code signing certificates to be used for signing files on Windows 7 and above starting January 1, 2016.
- Files signed previously with a SHA-1 certificate will continue to work on Windows 7 and above for an additional year as long as they were time-stamped before January 1, 2016.
- Windows 7 and Server 2008 R2 will require a hotfix for SHA-256 support.
- Starting on Jan. 1, 2017, all SHA-1 signed files will be blocked on Windows 7 and above, regardless of when they were time-stamped.
On Vista and Server 2008 platforms:
- Microsoft will execute end of life support for Vista on April 2017, and for Server 2008 on January 2020.
- SHA-1 certificates will be supported through the end-of-life for these operating systems.
- There will be limited support for SHA-256 on these platforms which will require a patch and only allows for downloads or installations of SHA-256 signed content.
The SHA-1 deprecation and SHA-2 support plans came as a result of the recommendation by National Institute of Standards (NIST). The recommendation was reinforced by recent tests showing that a SHA-1 certificate could be compromised with an investment for as little as $75K USD.
Symantec recommends replacing SHA-1 certificates with SHA-256 as soon as possible, where the operating systems support SHA-256. Make sure your default enrolment is SHA-256 and that any customer with a SHA-1 certificate can get a replacement SHA-256 certificate and vice versa, for free. This will allow your customers to have two valid certificates, SHA-1 and SHA-256.
24/02/2016 GlobalSign
Commencing from March 1st, 2016, GlobalSign will be discontinuing issuance of its DocumentSign for Adobe CDS Certificate with a 3 year validity period. This is due to Adobe ending support for its Certified Document Service (CDS) Program and in line with GlobalSign's SHA256 Intermediate CA for Adobe expiring in June 2019. 1 and 2 year validity period certificates will still continue to be available.
You can continue to use 1-2 year DocumentSign for Adobe CDS Certificates for the short term, or consider revising your offering to enable 1-3 year AATL DocumentSign Certificates
22/02/2016 Symantec
- Certificate Transparency support for all brands of DV products
- DNS Authentication support for Revocations of DV orders
- SAN Wildcard Support for all brands of OV SSL Products
18/02/2016 adgrafics
RC4 Cipher No Longer Supported. Within the last month, major browsers have removed support for the RC4 Cipher, which was an encryption algorithm available for SSL connections. Academic research found that this cipher had serious design flaws which could allow attackers to decrypt information using the cipher. Support for RC4 was officially dropped with Chrome v48 and Firefox v44, both released in late January. Microsoft’s Edge browser and IE11 will also be dropping support for the cipher.
18/02/2016 Google
The Chrome security team has added a new security panel on Chrome which will provide greater clarity to its SSL icon indicators, as well as help identify mixed content on a given secure site.
This should help clients better understand the details behind the green secure padlock ..
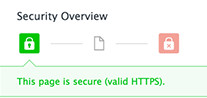
.. indicate mixed content and other partial secured connections ..
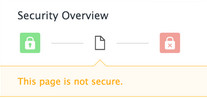
.. and recognize insecure web pages.
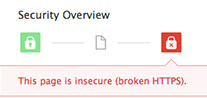
more of what has changed with the Chrome browser padlock in this regards Chrome Security Panel
02/02/2016 Symantec
The worldwide cybersecurity market continues it’s fast growth at almost 12% in 2016 (estimated to reach $30b worldwide).
03/02/2016 adgrafics
Over the past several years there has been increased discussion about deprecating HTTP and making HTTPS the default protocol for the World Wide Web. (HTTP stands for “HyperText Transfer Protocol” and the “S” in HTTPS is enabled with an SSL/TLS digital certificate properly installed and configured on a web server.)
03/02/2016 adgrafics
Moving to Always on HTTPS, Marking HTTP as Unsecure
14/01/2016 DV and OV Certificate Transparency
Symantec will be expanding Certificate Transparency support across all our brands of OV products on 19th January and all brands of DV products on 29th February 2016. Certificate Transparency helps to guard against several certificate-based threats such as mis-issued certificates and maliciously acquired certificates.
14/01/2016 New Symantec Intermediate cert
Symantec is introducing new intermediate certificates for the RapidSSL, RapidSSL Wildcard, QuickSSL and QuickSSL Premium products.
10/01/2016 SHA1 and 2016
Let's Encrypt certificates seen in sites that lead to banking malware Cybercriminals have begun abusing certificates issued by the certificate authority (CA) Let’s Encrypt to deliver banking malware
1/01/2016 SHA1 and 2016
On January 1, 2016, the public trust certification authorities (CAs) will stop issuing SHA-1 signed SSL/TLS certificates. What will happen? Will all websites using SHA-1 fail? No. SHA-1 will be supported by browsers and operating systems through 2016. Microsoft and Mozilla have announced that Windows and Firefox will not support SHA-1 in 2017, but no change for 2016. We expect Apple to follow the same protocol. What about Chrome? Chrome will still provide warning indications in the browser status bar for SHA-1 signed certificates which expire in 2016 and in 2017 or later. No change.
